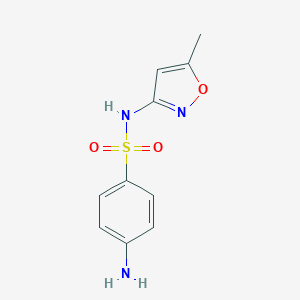
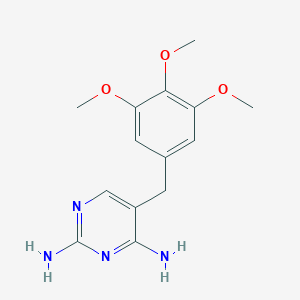
Acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, Acute uncomplicated urinary tract infections
Adult: Available preparation:
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg in 5 mL solution for infusion
For cases where there is bacteriological evidence of susceptibility and a good reason to prefer the combination instead of a single antibiotic: In patients unable to take oral treatment: 960 mg 12 hourly via infusion over 60-90 minutes. Severe infections: 2,880 mg daily in 2 divided doses. Continue until the patient is symptom-free for 2 days; most patients require treatment for at least 5 days. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg in 5 mL solution for infusion
For cases where there is bacteriological evidence of susceptibility and a good reason to prefer the combination instead of a single antibiotic: In patients unable to take oral treatment: 960 mg 12 hourly via infusion over 60-90 minutes. Severe infections: 2,880 mg daily in 2 divided doses. Continue until the patient is symptom-free for 2 days; most patients require treatment for at least 5 days. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Intravenous
Pneumocystis (carinii) jirovecii pneumonia
Adult: Available preparation:
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg in 5 mL solution for infusion
Treatment in patients unable to take oral treatment: 120 mg/kg daily in 2-4 divided doses via infusion over 60-90 minutes. Shift to oral therapy as soon as possible then continue for a total treatment period of 14 days. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg in 5 mL solution for infusion
Treatment in patients unable to take oral treatment: 120 mg/kg daily in 2-4 divided doses via infusion over 60-90 minutes. Shift to oral therapy as soon as possible then continue for a total treatment period of 14 days. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Oral
Acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, Acute uncomplicated urinary tract infections
Adult: Available preparations:
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
For cases where there is bacteriological evidence of susceptibility and a good reason to prefer the combination instead of a single antibiotic: 960 mg bid. Severe infections: 2,880 mg daily in 2 divided doses. Continue until the patient is symptom-free for 2 days; most patients require treatment for at least 5 days. Reassess patient if there is no clinical improvement after 7 days. Alternatively for acute uncomplicated lower UTI, short-term treatment duration of 1-3 days has shown to be effective. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Child: Available preparations:
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 200 mg and trimethoprim 40 mg per 5 mL oral susp
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
As 200 mg/40 mg per 5 mL susp: 6 weeks to 5 months 120 mg bid; 6 months to 5 years 240 mg bid; 6-12 years 480 mg bid. As tab or 400 mg/80 mg per 5 mL susp: >12 years Same as adult dose. Standard dose for children is equivalent to approx 30 mg sulfamethoxazole and 6 mg trimethoprim per kg daily in 2 divided doses. Continue until the patient is symptom-free for 2 days; most patients require treatment for at least 5 days. Reassess patient if there is no clinical improvement after 7 days. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
For cases where there is bacteriological evidence of susceptibility and a good reason to prefer the combination instead of a single antibiotic: 960 mg bid. Severe infections: 2,880 mg daily in 2 divided doses. Continue until the patient is symptom-free for 2 days; most patients require treatment for at least 5 days. Reassess patient if there is no clinical improvement after 7 days. Alternatively for acute uncomplicated lower UTI, short-term treatment duration of 1-3 days has shown to be effective. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Child: Available preparations:
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 200 mg and trimethoprim 40 mg per 5 mL oral susp
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
As 200 mg/40 mg per 5 mL susp: 6 weeks to 5 months 120 mg bid; 6 months to 5 years 240 mg bid; 6-12 years 480 mg bid. As tab or 400 mg/80 mg per 5 mL susp: >12 years Same as adult dose. Standard dose for children is equivalent to approx 30 mg sulfamethoxazole and 6 mg trimethoprim per kg daily in 2 divided doses. Continue until the patient is symptom-free for 2 days; most patients require treatment for at least 5 days. Reassess patient if there is no clinical improvement after 7 days. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Oral
Pneumocystis (carinii) jirovecii pneumonia
Adult: Available preparations:
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
Treatment: Up to 120 mg/kg daily in 2-4 divided doses for 14-21 days. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Child: Available preparations:
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 200 mg and trimethoprim 40 mg per 5 mL oral susp
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
>12 years Same as adult dose.
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
Treatment: Up to 120 mg/kg daily in 2-4 divided doses for 14-21 days. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Child: Available preparations:
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 200 mg and trimethoprim 40 mg per 5 mL oral susp
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
>12 years Same as adult dose.
Oral
Prophylaxis of Pneumocystis (carinii) jirovecii pneumonia
Adult: Available preparations:
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
960 mg once daily for 7 days, or 960 mg once daily 3 times a week on alternate days, or 960 mg bid 3 times a week on alternate days. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Child: Available preparations:
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 200 mg and trimethoprim 40 mg per 5 mL oral susp
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
As 200 mg/40 mg per 5 mL susp: 6 weeks to 5 months 120 mg bid for 7 days, or 120 mg bid 3 times a week on alternate days, or 120 mg bid 3 times a week on consecutive days, or 240 mg once daily 3 times a week on consecutive days; 6 months to 5 years 240 mg bid for 7 days, or 240 mg bid 3 times a week on alternate days, or 240 mg bid 3 times a week on consecutive days, or 480 mg once daily 3 times a week on consecutive days; 6-12 years 480 mg bid for 7 days, or 480 mg bid 3 times a week on alternate days, or 480 mg bid 3 times a week on consecutive days, or 960 mg once daily 3 times a week on consecutive days. As tab or 400 mg/80 mg per 5 mL susp: >12 years 960 mg bid for 7 days, or 960 mg bid 3 times a week on alternate days, or 960 mg bid 3 times a week on consecutive days, or 1,920 mg once daily 3 times a week on consecutive days. The daily dose given on treatment day is approx 750 mg sulfamethoxazole/m2/day and 150 mg trimethoprim/m2/day. Max: 1,920 mg daily. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
960 mg once daily for 7 days, or 960 mg once daily 3 times a week on alternate days, or 960 mg bid 3 times a week on alternate days. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Child: Available preparations:
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 200 mg and trimethoprim 40 mg per 5 mL oral susp
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
As 200 mg/40 mg per 5 mL susp: 6 weeks to 5 months 120 mg bid for 7 days, or 120 mg bid 3 times a week on alternate days, or 120 mg bid 3 times a week on consecutive days, or 240 mg once daily 3 times a week on consecutive days; 6 months to 5 years 240 mg bid for 7 days, or 240 mg bid 3 times a week on alternate days, or 240 mg bid 3 times a week on consecutive days, or 480 mg once daily 3 times a week on consecutive days; 6-12 years 480 mg bid for 7 days, or 480 mg bid 3 times a week on alternate days, or 480 mg bid 3 times a week on consecutive days, or 960 mg once daily 3 times a week on consecutive days. As tab or 400 mg/80 mg per 5 mL susp: >12 years 960 mg bid for 7 days, or 960 mg bid 3 times a week on alternate days, or 960 mg bid 3 times a week on consecutive days, or 1,920 mg once daily 3 times a week on consecutive days. The daily dose given on treatment day is approx 750 mg sulfamethoxazole/m2/day and 150 mg trimethoprim/m2/day. Max: 1,920 mg daily. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Oral
Acute otitis media
Child: Available preparations:
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 200 mg and trimethoprim 40 mg per 5 mL oral susp
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
As 200 mg/40 mg per 5 mL susp: 6 weeks to 5 months 120 mg bid; 6 months to 5 years 240 mg bid; 6-12 years 480 mg bid. As tab or 400 mg/80 mg per 5 mL susp: >12 years Same as adult dose. Standard dose for children is equivalent to approx 30 mg sulfamethoxazole and 6 mg trimethoprim per kg daily in 2 divided doses. Continue until the patient is symptom-free for 2 days; most patients require treatment for at least 5 days. Reassess patient if there is no clinical improvement after 7 days. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg tab
Sulfamethoxazole 200 mg and trimethoprim 40 mg per 5 mL oral susp
Sulfamethoxazole 400 mg and trimethoprim 80 mg per 5 mL oral susp
As 200 mg/40 mg per 5 mL susp: 6 weeks to 5 months 120 mg bid; 6 months to 5 years 240 mg bid; 6-12 years 480 mg bid. As tab or 400 mg/80 mg per 5 mL susp: >12 years Same as adult dose. Standard dose for children is equivalent to approx 30 mg sulfamethoxazole and 6 mg trimethoprim per kg daily in 2 divided doses. Continue until the patient is symptom-free for 2 days; most patients require treatment for at least 5 days. Reassess patient if there is no clinical improvement after 7 days. Consideration must be given to local treatment guidelines on the appropriate use of antibacterials. Dosage recommendation may vary among individual products or between countries (refer to detailed product guideline).




 Sign Out
Sign Out